The program is almost completely automated process of collecting wind load applied to the beam structures. Wind to the beam structures can be applied in two ways: either loading surface or directly to the rod or cable-stayed elements. The program has built-in effective calculators allow, depending on the type of structure, calculate the aerodynamic coefficients and correlation coefficients of windward surfaces.
But even more effective use of the program when the load is applied directly to the core elements and cables. To specifying such loads it is necessary to give only general characteristics of wind flow: wind area and normative pressure. Everything else the program defines itself. While it takes into account the orientation of the rod relative to the wind flow, the shape and dimensions of the rod, the section orientation, the position of the rod relative to the earth's surface, depending on the speed of wind flow and form of section calculates the aerodynamic coefficient, find its shading surfaces and calculates the shading coefficient.
In addition, especially for the formation of wind load on a structure intended to serve the radio-relay networks, finite pseudo element of antenna is entered in the program, whose sole function - generate and transmit wind load on the structure. The program maintains a database of typical antennas, numbering about 2,500 antennas from different manufacturers. If necessary, the user can fill this base oneself.
 |
Panel High band antennas |
 |
Directional antennas (Yagi, Logo, Helix) |
 |
Omnidirectional antennas |
 |
Panel Low band antennas |
 |
Dipole antennas |
 |
Turnstile antennas |
 |
RRL antennas |
 |
Remote units |
| |
|
|
Fluctuating component of the wind action is also formed extremely easy - just specify the number of the static loading which corresponds to the static wind component. The program will automatically convert static component in fluctuating oneself. The results of the analysis are the amplitudes of the nodal displacements, forces and stresses in the elements of the current wind pulsation components. These results correspond to the the level of static load component of the wind loading - normative values of the static component correspond to normative values of the pulsation components, the calculated – to calculated.
( ReadReduce )
 Wind resonans
Calculation of the tower structures and chimneys due to the vortex excitation (wind response).
Under certain wind speeds generated vortex shedding from the lateral edges of the structures (towers, chimney), who begin to rock structure in the transverse direction relative to the wind flow. The most dangerous is the condition where the vortex shedding frequency coincides with one of the natural frequencies of the structure.
The regime allows you automatically form a dynamic load acting across the wind flow. In addition, the program automatically generates static and pulsation wind components, corresponding to a given resonance effects.
( ReadReduce )
 Seismic
Calculation on seismic action is performed based on the linear-spectral method. The calculation can be made in accordance with the requirements of SNiP II-7-81, DBN B.1.1-12: 2006 and NP-031-01.
In all cases, the inertial load is decomposed according to the mode shape of building. For each mode of vibration the dynamic factor is introduced, calculated on the basis of spectral properties of the seismic action and a number of factors, taking into account the structural features of buildings.
The results of analysis are the amplitudes of the nodal displacements, forces and stresses in structural elements.
( ReadReduce )
 Lanes
Construction and rolling-on the lanes. The program allows you to build and produce lanes knurled of displacements, efforts, stresses and support reactions.
To construction the lane it is necessary to build routes of the lanes knurling. The user can specify any number of independent routes simultaneously.
The mobile load is formed as a series of vertical forces. Each force is tied to a particular route and fixes respect to the first force, entered on the route.
( ReadReduce )
 Cable structures calculations
The program performs both static and dynamic analysis of cable and cable-stayed grid nets. The program can solve equally well the problems as with highly stretched strings and with hanging down heavily cables because the exact solution for the rope is laid as a basis of solution. Also another feature of the program is that the rope may be considered as multimass system, which enables to adequately take into account its interaction with the structure under dynamic effects.
In addition to ordinary static and dynamic calculations the program provides a number of specialized calculations for cable structures, making it possible not only to check the bearing capacity of the structure, but also to pick up its options at the best way.
( ReadReduce )
 Cable grid net calculation
Under a cable grid net is understood the systems, some nodes of which are formed exclusively by jointed ropes (threads). Masses and dampers may be attached to these nodes, but any other elastic elements can’t be attached to them. It can be various grids attached to an elastic structural elements, dangling threads, dangling grids. If, for example, guy lines of mast subdivided into several sections, that this system has to be regarded as a cable grid net.
Cable grid net – it is significantly more difficult objects in terms of analysis than just a cable system. The program implements an efficient algorithm for analysis of cable grid nets of any complexity. With the same success the program solves both static and dynamic problems. For example, in the accompanying this item demo shows the movement of freely suspended grid after being hit by massive body.
( ReadReduce )
 Adjusting the tension of the guys
This mode allows you to build a program of guys tension adjustment (cable-stayed guy), if we know the initial tension of the guys, and the design tension, corresponding to a given load. If the structure contains n controlled cable-stayed elements, the control program permits you to go from initial state to a final in n steps.
To perform the calculations it is necessary to set the initial tension of the guys, the guys design tension, and adjusting order. The result of the calculation is the values of guy’s tension in adjustment process.
( ReadReduce )
 Defining project tension guys for masts
This mode allows you to determine the optimal design guy’s tension for masts. Algorithm of solution constructed in such a way that provides the desired deformation of the mast at the lowest pressing force of structure, which positively affects on the construction buckling.
The program can work in two modes: the selection of cable tension with the given cables’ parameters and selection cables’ tension with parallel selection ropes’ section. The result of this calculation is the design cables tension, optimal cables section and stress state on all construction by all specified static loadings.
( ReadReduce )
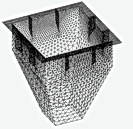 Shells generation
The program allows you to create different kinds of shells, covering them with high-quality triangular meshes. 8 different types of generation facilities:
|
 |
Generation of spheres |
 |
Generation of surfaces of revolution |
 |
Generation of shallow shells of revolutio |
 |
The generation of planes |
 |
Generation by translationй |
 |
Generation of quadric surfaces |
 |
Generation of surfaces given by algebraic expression |
 |
The generation of surfaces in the assembly |
| |
|
|
You can use concentrators and introduce fixed nodes into the mesh. The software allows to built shells intersection and cut them by different bodies. Generation of assembly allows you to generate a group of planes, forming a kind of coherent structure (for example, a node structural). The program itself provides the conjugation of planes boundaries. Several independent areas can be generated simultaneously. Relative location of independent regions can be completely arbitrary.
( ReadReduce )
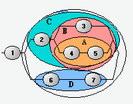 Combinations of loads
Combinations - finding the most unfavorable combination of loads in concordance with various calculation factors. The calculated combination may include simultaneously static, harmonic, pulsation wind, seismic loading, a stationary random process, the dynamic random effects, lanes rolling.
Calculation of the unfavorable combination of loads is performed based on the combination of graphs. The graph is represented by combinations of a set of points that are pairwise connected by segments of curves (arcs). Each arc of the combination graph means a loading, on the action of which had been calculated. The combination of loads is depicted in the graph as a continuous sequence of arcs forming a path from the initial vertex to the destination. The result of calculation for each item are the maximum (minimum) value for each selected calculation factors (force, stress), the corresponding forces and stress and loadings combinations, which ensured the extreme value of the estimated factors.
( ReadReduce )
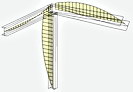 Construction the diagrams of warping and bimoment on finite element models of rods
The program allows you to build the diagrams of warping and bimoment on finite element models of rods. Each rod is divided onto 20 sections and according to the results of analysis of finite element model the integrals are calculated
where d и В - warping and bimoment in the section, un and sn - normal displacements and normal stresses in the cross section, w - sectorial coordinate of the section point, Jw - sectorial moment of inertia. This feature is useful for the construction units analysis.
( ЧитатьСвернуть )
 Vibromonitorig
In engineering practice, there is often appear a problem - to assess the functionality of a structure on which a certain production line is installed, including rotating elements: rotors of motors, shafts, drums, etc. The effect of such elements is the increased vibration of the structure, which in some cases may even lead to its destruction. The cause of the vibration is small eccentricities of rotating elements that cannot be measured "manually". The task is to build an adequate design scheme for the excitation of a structure based on indirect telemetric measurements.
Due to the possibility of setting the dynamic centrifugal inertia forces in the program, and the built-in module of treatment of stationary random processes, the vibration monitoring mode allows you to reconstruct the real scheme of the structure excitation based on the accelerograms. That makes it possible to predict the work of the structure in other heavier modes.
( ЧитатьСвернуть )
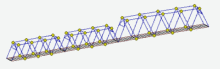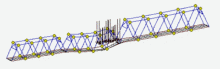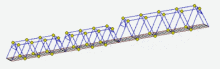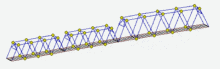 Moving dynamic load
To perform calculation on the moving dynamic load it is necessary to build lanes routes. The user can specify any number of independent routes simultaneously, and to put on them independent dynamic forces, synchronize them in time.
Inertia of the moving mass is ignored. However, the values of the driving forces can be added by the component varying sinusoidal. The frequency of the dynamic component can be specified for each individual force. It can be set either a cophasal, or a random-phase mode changed dynamic component of the moving forces.
The results of this analysis are the diagrams changes over time of nodal displacements, forces and stresses in structural elements. The overall picture of deformation can be represented in a multiplicative way.
( ReadReduce )
|